FHIR Implementation Guide for Stroke - Local Development build (v0.0.0) built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) Build Tools. See the Directory of published versions
ICHOM
Introduction
The International Consortium for Health Outcomes Measurement (ICHOM) aims to empower value-based healthcare by defining globally a Patient-Centered Health Outcome Measure Sets, which involve considerations of outcomes reported by healthcare professionals as well as patients, in order to promote the adoption, reporting, and benchmarking of these measures on a global scale, with the goal of generating better health outcomes for all involved.
So far, Patient-Centered Health Outcome Measure Sets have been defined for 45 different clinical conditions and specific patient populations through the gathering of global teams of patient advocates, healthcare professionals, and researchers, representing more than 50% of the global disease burden, as described on this page.
To facilitate the adoption and implementation of these ICHOM Patient-Centered Health Outcome Measure Sets in healthcare, health information technology systems need them to be published in an interoperable form, and in a machine-readable format based on open standards. This will facilitate the semantically interoperable collection of the necessary measurements along the patient care pathway, as well as the subsequent reporting of outcomes based on these measurements. With this goal, ICHOM created the Patient-Centered Health Outcome Measure Set for Stroke. It is believed that the international reach of ICHOM's standard sets will allow their use, adoption, and global implementation in clinical practice.
Background
There is an increasing necessity to represent ICHOM's Patient-Centered Health Outcome Measure Sets through HL7 FHIR APIs for the global community. The clinical elements within ICHOM's Patient-Centered Health Outcome Measure Sets have been established and endorsed based on international clinical research. These elements have undergone a patient-focused process and have been critically reviewed by experts, ensuring their alignment with standard ontologies, such as SNOMED-CT.
The purpose of this FHIR IG is to formulate and disseminate a HL7 FHIR representation, integrating the stroke clinical pathway with the ICHOM’s Patient-Centered Outcomes Measure Set for Stroke. The initiative is dedicated to enhancing data interoperability, which is crucial for evaluating value-based healthcare practices. This initiative aligns with the standards set by ICHOM’s international expert community, responsible for the creation of this comprehensive data set.
ICHOM’s Patient-Centered Health Outcome Measure Sets for Stroke
This Implementation Guide in the knowledge domain focuses on representing the same variables from the Patient-Centered Health Outcome Measure Set for Stroke in two different ways:
- 1) as FHIR Questionnaires for patient-reported outcomes and clinically reported outcomes, and
- 2) as FHIR Profiles for clinically reported outcomes.
Moreover, implementers are afforded the flexibility to choose between implementing the questionnaires, the profiles, or both, based on their specific needs.
Definitions
* PROM (Patient-Reported Outcome Measure): A scientifically validated questionnaire that assesses specific aspects of a patient's health experience. Scores are assigned to each response, and these scores are totaled based on a published algorithm. Typically, both individual question responses and summarized scores are saved, but analyses are only performed on the summarized scores. Example: PROMIS Global.
* Third-Party Providers: Typically, technology or analytics companies that offer a platform to meet specific data collection or analysis needs, such as collecting patient PROMs data.
* Learning Collaboration: A quality improvement activity where provider organizations agree to privately share their de-identified patient outcome data with the aim of facilitating conversations and learning best care practices from each other.
Questionnaires
The Questionnaires in this FHIR IG are organized differently from the ICHOM Reference Guide and Data Dictionary, and this is due to different emphases or intended uses. The Reference Guide and Data Dictionary are designed to describe all data elements included in the set, so they are organized by data type or variable. In contrast, this FHIR IG is intended to facilitate the collection of data elements. Therefore, it is organized based on the timing of patient health data collection during their care journey; for example, at 'baseline,' at '1-year follow-up,' and based on the data source (clinical or patient-reported). Despite this difference in organization, the data elements in the FHIR IG and the ICHOM Reference Guide and Data Dictionary are completely aligned. The questionnaires have been divided into two major groups: Patient-reported questionnaires with data collection at the following time points: baseline, discharge or 7 days, and 90 days; and Clinician-reported questionnaires with data collection at the following time points: baseline, discharge or 7 days, 90 days, and annual update, as illustrated in Figure 1.
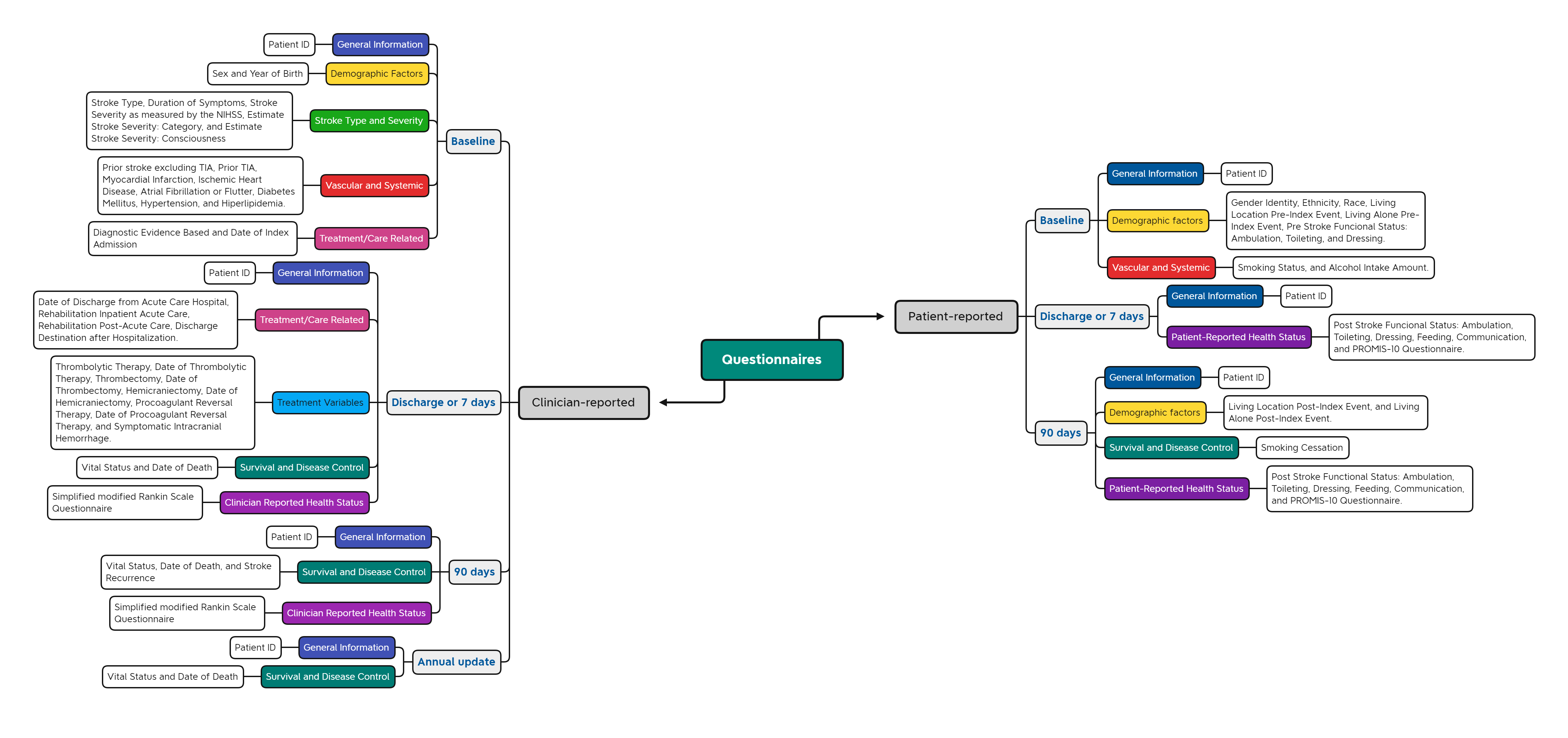
|
|---|
Figure 1 – Structure of Questionnaire in the FHIR IG for Stroke.
Profiles
The Profiles adhere to the ICHOM reference guide and data dictionary organization, as well as to the Profiles of the Brazilian National Data Network. Each variable is mapped to a singular FHIR resource, whereas multiple variables may be mapped to the same FHIR resource. The mappings themselves are conveyed using a FHIR profile, as shown in Figure 2.
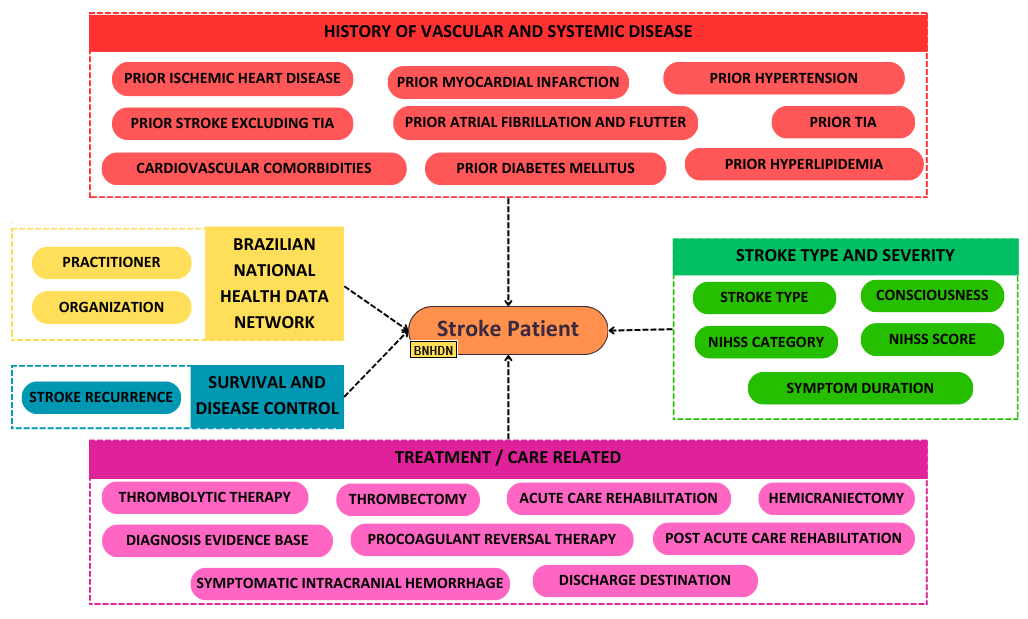
|
|---|
Figure 2 – FHIR Profiles for Stroke: Alignment with ICHOM Data Set and Brazilian National Data Network.
IP Statements
This publication includes IP covered under the following statements.
- Copyright HL7. Licensed under creative commons public domainShow Usage
- This material contains content from LOINC. LOINC is copyright © 1995-2020, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. and the Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) Committee and is available at no cost under the license. LOINC® is a registered United States trademark of Regenstrief Institute, Inc.Show Usage
- This material contains content that is copyright of SNOMED International. Implementers of these specifications must have the appropriate SNOMED CT Affiliate license - for more information contact https://www.snomed.org/get-snomed or info@snomed.org.Show Usage